Strategic Management Consulting
Financial institutions face a wide range of business and operational challenges due to a multitude of factors:
- Rapidly changing consumer preference due to demographic shifts and new market disruptions requires financial institutions to rethink their product and delivery strategy;
- Digital innovations are disrupting the financial services sector, necessitating new supervisory approaches and financial market innovations;
- Regulators and other stakeholders are increasingly factoring environment, social and governance (ESG) aspects of financial institutions into their assessments of business performance.
While these challenges may bring about uncertainty to financial institutions, we see them as presenting opportunities to a new realm of profitability and growth, if they are properly harnessed and managed.

Overview
ESG – or ‘environment, social and governance’ – has become a popular shorthand for the wide range of non-financial factors affecting businesses and investors’ success. It represents a set of criteria organisations use as standards to manage their business and operations responsibly and report the outcomes of their ESG practices to be socially accountable to their stakeholders and the public.
The ESG regulatory race has begun. In support of the UN 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development and the Paris Agreement on climate change, governments are making strides to accelerate the low-carbon transition on a global scale and implementing regulations to improve transparency in areas around diversity and inclusion. Investors are favouring organisations with a clearly articulated ESG framework. Consumers are attracted to brands with sustainable practices and ethical values, and employees are seeking greater equality, empowerment and better conditions in the workplace.
From a risk management perspective, climate risk is distinct subset stemming from the ESG discussions. Climate risk represents the financial risk that arises from climate change, it can affect financial balance sheets and lead to losses through diminished asset valuations and/or increased loan defaults. With time gradually inching closer for nations to reach net-zero emissions pledge by 2050, more environmental regulations and sustainable financing practices are expected to be rolled-out in quick succession.
With these factors driving the ESG agenda, organisations need to take a forward-looking and comprehensive approach to considering climate-related and environmental risks, and holistically integrate ESG goals into their strategy, operations and value chain. Failure to act on sustainability may negatively impact an organisation’s operational and financial performance, resilience and business longevity, and reputation and public perception.
Our Services
We assist our clients to craft an organisation-wide response plan to ESG and Climate Risk, from governance, strategy, risk management to disclosure, as listed below:
- Review and enhance governance framework in line with organisations’ ESG and climate risk agenda. This includes reviewing terms of reference and risk appetite statement to align board and senior management’s roles and responsibilities and KPIs to organisation’s climate and ESG goals.
- Conduct an end-to-end recalibration of organisations’ existing risk management cycle to ensure that climate risks arising from own and customer’s operations are identified, measured, monitored and reported. We develop end-to-end solutions to assist organisations with day-to-day ESG and climate risk management activities, such as:
- ESG scoring and risk assessment framework,
- Climate risk transmission channels mapping,
- Climate and emission measurement metrics; and
- Risk limits / threshold and escalation framework.
- Assist organisations in meeting their regulatory climate risk stress testing requirements. This includes reviewing modelling methodology and climate data reliability assessment.
- Advise organisations to embed ESG issues into their corporate strategy. We will review organisation’s portfolios and product lines to ensure alignment with consumer sustainability preferences and any opportunities arising from their countries’ climate policy.
- Perform ESG and climate-focused data gap analysis by assessing organisations’ operational readiness and capabilities in collecting and processing relevant, high-quality data. We will provide recommendations on closing these data gaps by establishing new data collection processes and identifying suitable data vendors for their risk management, disclosure and strategy setting needs.
- Assess organisations’ ESG and climate risk disclosure maturity level. To help them meet their sustainability reporting expectations, we will assist to align their sustainability disclosures and accompanying narratives with organisational strategy and country-specific mandatory disclosures, as well as to adopt industry best practices and globally recognised standards such as TCFD and GHG Protocol that complement their disclosures.
- Provide independent review and assurance over organisations’ sustainability, ESG and climate-related reporting and disclosures.
- Develop and conduct training programmes on climate risk and reporting, ESG framework and board diversity for the board and senior management, to help them understand and navigate the continuously evolving regulatory landscape concerning sustainability reporting requirements and emerging best practices.
Customer Segment Management
Overview
Basel capital framework implementation has re-emphasized the retail banking business, as Individual Banking and SME Business Banking segments that are managed on a portfolio basis may benefit from generally lower capital requirements under the framework.
These segments are characterized by a large and diverse customer base. As such, it requires banks to develop a well-articulated strategy and customer intelligence to gain deep understanding of customer profile and needs, so as to deliver the right products and services. To maximise returns from these segments, an effective operating model needs to be implemented.
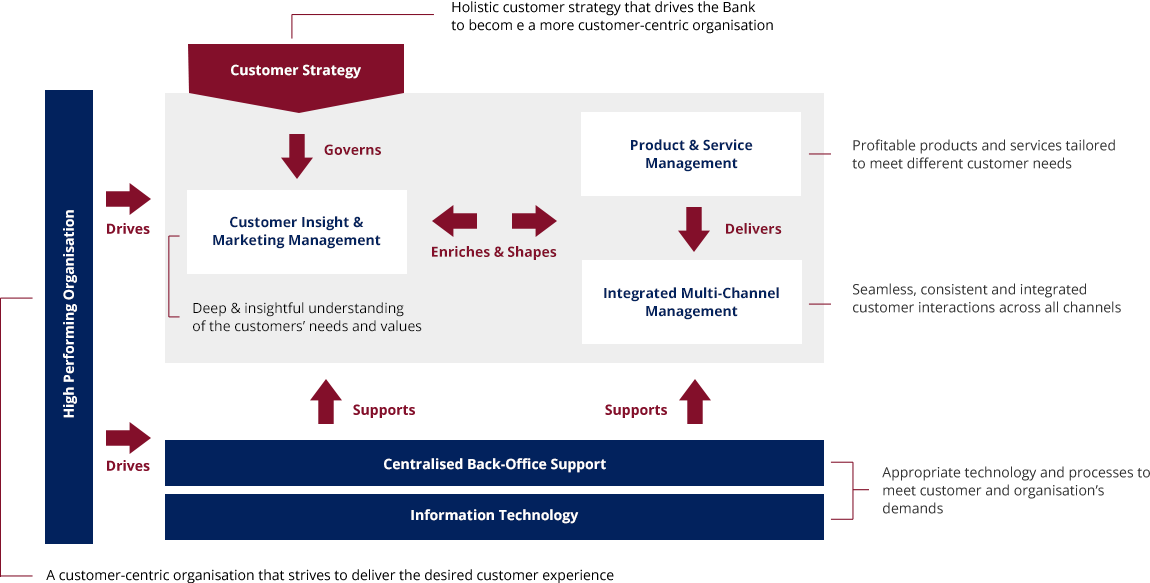
Effective execution of a retail banking strategy and operating model will require a clear definition of how the front-, middle- and back-offices interact. Many banks have successfully adopted Customer Relationship Management (CRM) initiatives to create an integrated operating model, linking the front-, middle- and back- offices, to provide superior customer experience, ensure effective cross-sell and deliver appropriate products and services to the right customers at the right time.
CRM is an integrated, enterprise-wide capability that is developed around customer-centric strategies, well thought-out business models, operating processes and technology, with the aim of maximizing profitability through enhanced customer value and increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Our Services
Our CRM Capabilities Framework will facilitate the identification of CRM capability gaps and subsequent development of an integrated CRM Blueprint and Implementation Roadmap for the Individual Banking or SME Business Banking segments.
Our CRM Blueprint and Roadmap development project will assist banks to benchmark its current organizational structure, capabilities and processes against industry practices and take stock of existing processes to determine how it supports / impedes fulfillment of corporate objectives.
In addition to the development of CRM Blueprint and Roadmap, we also provide the following consultancy services to assist our clients in their CRM journey for the Individual Banking or SME Business Banking segments:
- Design detailed CRM capabilities across all channels, including organization, processes, technology platform (in conjunction with strategic partner providing CRM platform/systems or with bank’s internal IT team), etc.
- Develop detailed functional requirements for the CRM core system, and re-design workflows for key processes to be used by the branch sales and service teams.
- Develop Effective Salesforce Model, including sales force Incentive and Compensation models, cross-sell and referral models for sales and service teams.
- Develop integrated multi-channel distribution strategy and bankwide customer service initiatives.
- Develop Customer Segmentation Strategies, Campaign Management and Product Development framework and processes to increase marketing effectiveness across all customer segments and products.
- Rationalize and streamline front-, middle- and back-office processes to provide more relevant and effective support for the CRM and customer-centric initiatives.
- Overall program management for the entire CRM implementation based on best-practice project management methodologies.
Wealth Management (Individual Banking)
Overview
Our Services
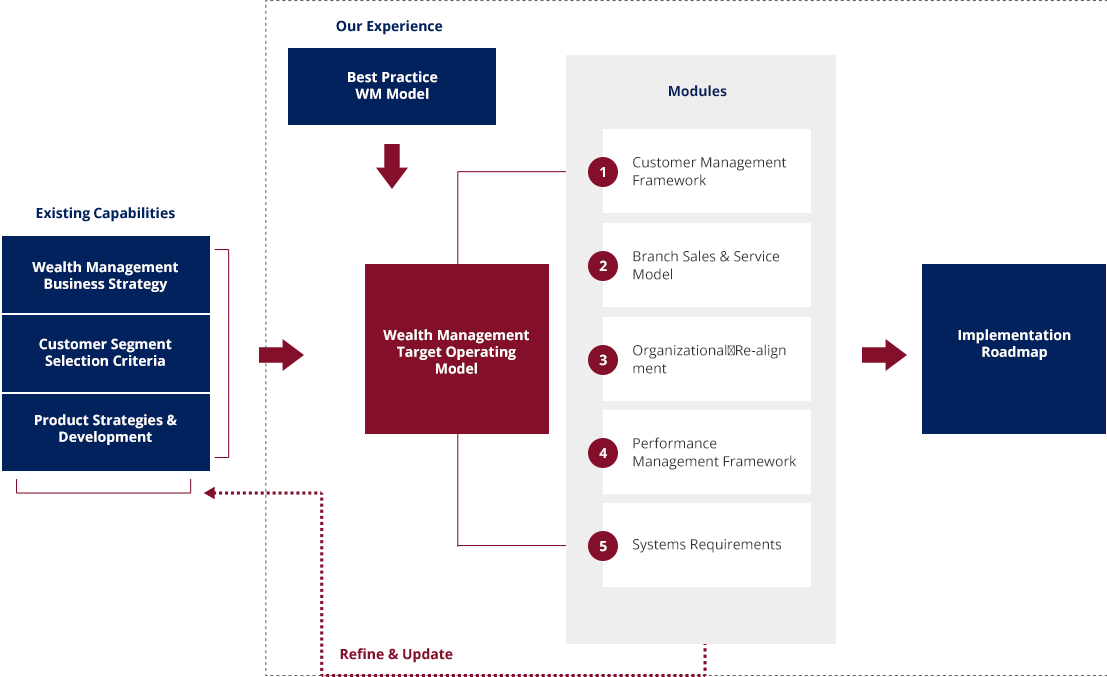
- Perform gap analysis for As-Is Wealth Management related capabilities against our Wealth Management Framework and existing industry practices, and identify areas of opportunities.
- Identify and prioritize opportunities for enhancing the bank’s wealth management capabilities.
- Develop implementation roadmap to address the opportunities for enhancement based on the Wealth Management Business Model.
- Develop the bank’s Wealth Management Business Model that will include the following key components:
Overview
To consistently achieve the optimal results from both the organisation’s business units and individuals, sound processes should be in place to drive the right behaviour and conduct. It is therefore important to align the organisation’s resources, processes, systems and employees to its strategic objectives and priorities.
To ensure that different business units and individuals are assessed fairly, the types and magnitude risks assumed should be taken into account when measuring returns achieved. This ensures that individuals remain cognisant of risks while pursuing business and financial goals.
The key components of a performance management framework will typically include the following three areas:
- RAROC Implementation
RAROC is one of the most commonly used risk-based measures of return and can be used to assess investment options and pricing on a forward looking basis (ex-ante), and measure performance on a backward looking basis (ex-post) when reviewing the performance of business units.
- Revenue and Cost Allocation
Proper revenue and cost allocation to each business unit is important as it enables a bank to accurately measure the profitability and performance of business units. This would in turn assist the bank in the optimal allocation of its resources, by directing resources to the more profitable business lines or segments.
- Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP)
FTP is a management tool that addresses a number of key issues, particularly the setting of the appropriate cost of funds to the respective business units, the transfer of liquidity and interest rate risks from the business units to be centrally managed by the Pool Fund Manager, and performance measurement.
Our Services
As part of the organisation’s performance management framework, we offer consulting services in the following areas:
- RAROC Implementation
Review and enhancement/development of the framework and methodology for RAROC computation and approaches for bank-wide implementation, including the following:- Cascading of RAROC targets to business units,
- Setting of hurdle rates,
- Integration with existing business processes (eg, credit approval, risk-based pricing, portfolio management/adjustment, etc),
- Segment/customer/product profitability assessment,
- Portfolio limit setting,
- On-going measurement, monitoring and reporting.
- Revenue and Cost Allocation
Review and enhancement/development of allocation framework and approaches, such as:- Determining the types of allocation method (Full or Partial) to adopt,
- Number of levels of indirect revenue/cost centres,
- Selection of the most relevant revenue/cost drivers to establish the basis for allocation,
- Applying actual levels or targeted levels of revenue/cost drivers for allocation.
- Funds Transfer Pricing (FTP)
Review and enhancement/development of FTP framework, including the following:- Methodologies and assumptions,
- Appropriate FTP governance structure,
- Data requirements,
- Components of FTP rates, such as market rates, liquidity transfer pricing (liquidity premium and liquidity cost of carry), etc.
Overview
Asia-Pacific region economies are growing rapidly, providing vast opportunities with an emerging middle-class amid rising income level. Businesses with the right strategies, products/services and people who have good knowledge of the region stand a better chance to benefit from growth arising from such opportunities.
Our Services
We leverage on our deep understanding of the financial services industry across the Asia-Pacific region, and wide network of contacts in the region to assist our clients in the following areas:
- Development of corporate and business strategies to tap opportunities in the region
- Identification of opportunities for strategic alliance and business tie-ups
- Business case analysis and evaluation
- Due diligence management
- Integration of business functions (eg, Product and Network Rationalisation)
- Market entry, including regulatory/licensing applications
- Regulatory and financial centre development
- Enhancement of the management of counterparty credit risk in event of member default at exchanges and clearing houses
- Enhancement of liquidity risk management of clearing houses

