Risk Management Consulting
Recent events in the financial industry have highlighted the importance of the risk management function:
- In the financial industry, regulators are setting higher standards for financial institutions’ risk management practices and internal control requirements, to tackle both traditional and emerging risk management topics
- Regulators and stakeholders (eg: shareholders, bondholders, customers, employees and partners) are expecting companies to comply with enhanced corporate governance, risk management and climate risk disclosure requirements.
Effective risk management requires the Board of Directors and senior management team to have a clear understanding of the risks taken by their organisation, and to have appropriate governance and reporting processes in place.
There is a need to embed risk management processes within the corporate decision-making structure so that risks can be monitored and managed in an ongoing manner.

Overview
To ensure that all risk exposures are adequately identified, measured, monitored and controlled, it is essential that a robust ERM Framework is formalized and implemented in the institution. This includes:
- Effective risk oversight from the Board and senior management
- Proper organization structure, including the 3 lines of defence
- Identification and measurement of various aspects of risk
- Robust risk monitoring
- Comprehensive risk reporting
- Establishment of appropriate risk limits
- Adequate internal controls
Such a framework requires the involvement of everyone in the institution, including the Board and senior management, and staff from the various business and support units.
The following are key components of a commonly adopted ERM Framework:
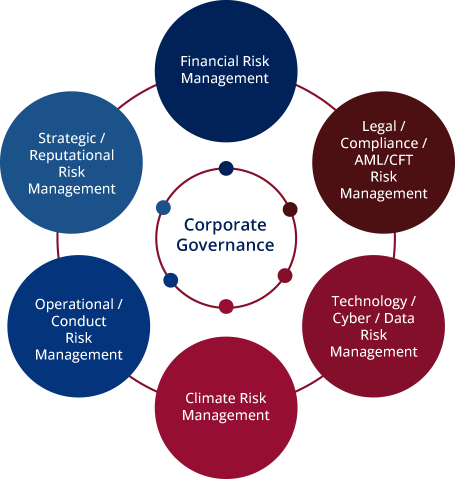
Corporate Governance: Provides the policies and processes by which organizations are managed and controlled. It specifies the roles and responsibilities among different stakeholders and the rules and procedures for decision making. It also covers the way in which the organisation’s actions, decisions and performance are monitored, reported and disclosed.
Strategic Risk: The organization’s ability to achieve strategic objectives or execute strategy, and to analyse and evaluate external factors that impact the strategy of the organisation.
Financial Risk: Depending on the nature and complexity of the organization’s business operations, Financial Risk may include Market Risk, Credit Risk, Liquidity Risk, Interest Rate Risk and/or Insurance Risk, etc.
Operational Risk: Material Operational Risk categories include internal processes and systems, human factors and external events.
Technology Risk: This arises from the use of technologies such as computer hardware, software, electronic devices, online networks and telecommunications systems, and the risk of systems failures, processing errors, software defects, operating mistakes, hardware breakdowns, capacity deficiencies, network vulnerabilities, security shortcomings, internal sabotage, espionage, malicious attacks, hacking incidents, fraudulent conduct and defective recovery capabilities, etc.
Compliance Risk: This arises from the organisation’s failure to comply with laws, regulations, industry codes of practice, and internal standards and guidelines.
Climate Risk: This arises due to physical effects resulting from climate and weather change (physical risk) or from efforts to mitigate or eliminate climate change (transition risk). Climate risk can cause financial losses through standard risk channels, such as diminished asset valuations, increased loan defaults or damaged properties.
Our Services
We assist our clients to develop and operationalise the following frameworks, taking into account their specific business, operational and regulatory requirements:
- ERM Framework
- Corporate Governance Framework
- Internal Control Framework
- Compliance Monitoring Framework
We also assist in formulation and establishment of management structure in line with local and international corporate governance best practices, taking into account of capability and structure of the client’s existing risk management functions.
With respect to climate risk, we offer consulting services to identify relevant climate risk drivers (in terms of physical and transition risk) and their transmission channel to tradition risk types (credit, market, operational and liquidity risk). Based on these inputs, we then help organization to enhance their existing ERM and risk management cycle, to manage and report climate risk drivers with the greatest impact.
For banking institutions, apart from the development of ERM Framework, we offer consultancy services across the entire spectrum of risk areas identified within the framework, as illustrated in the following diagram:
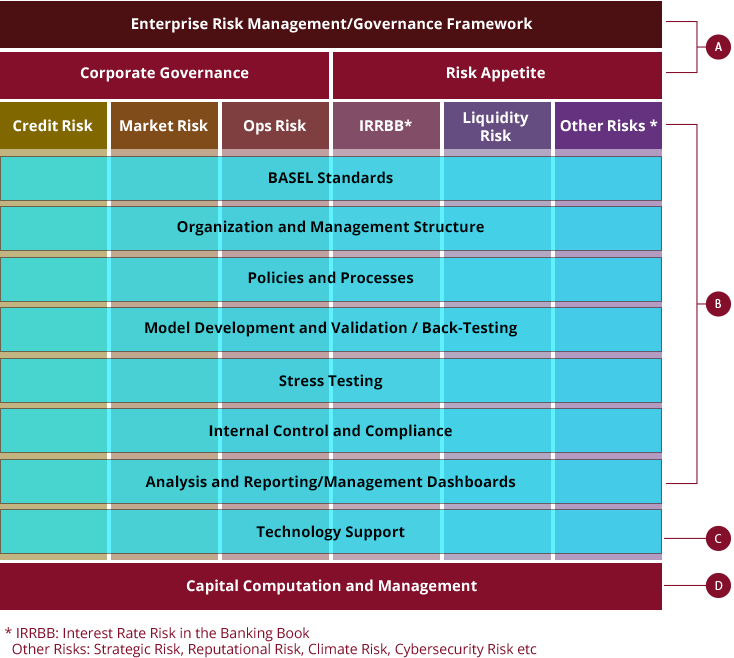
A
- Set and review risk appetite
- Review/enhance corporate governance framework (organization, reporting lines, roles and processes, etc)
- Review/enhance enterprise risk management (policies, guidelines, reports, processes, etc)
B
- Review current situation and gaps
- Enhance/develop policies & processes
- Develop/validate Models
- Review internal control and compliance
- Define portfolio management and reporting requirements, etc
C
- Define RFP requirements
- Assist in vendor evaluation
- Develop Functional Specifications
- Implementation jointly with system vendors
D
- Assess existing capital planning and target setting process
- Develop integrated capital management framework and processes to assess optimal level of capital
The development of the bank’s ERM Framework will typically encompass the following key steps:
- Review current risk management framework, policies and gaps. A comprehensive gap report will be developed to document in detail the gaps identified and possible areas of enhancement and improvement.
- Enhance/Define risk management framework, including setting up of a proper risk governance structure.
- Enhance/Develop bank-wide risk management policy framework, by recalibrating existing risk identification, measurement, mitigation and reporting process of the organization, to manage emerging risk types such as climate risk and cybersecurity risk.
Overview
Credit risk refers to the potential loss arising from any failure by customers to fulfill their obligation, as and when they fall due. The major components of Credit Risk Management include the following:
- Organizational Controls
- Robust Process for Credit Analysis and Approval
- Risk-Based Pricing
- Monitoring of Portfolio Quality
- Portfolio Management, including Limits on Concentration
- Stress Testing
- Collection and NPL Management
Our Services
Our Services in relation to Credit Risk Management include the following (please also refer to details under Basel Capital Framework):
- Assessment of the bank’s current operating environment in all aspects of Credit Risk Management, including gaps and changes required for the bank to qualify for Internal Ratings-Based (IRB) approach under Basel Capital Framework.
- Review of Credit Policies, Credit Controls, Processes, Systems and Management Reporting
- Development and validation of credit models in line with Basel standards, including:
- Rating models for Corporate, SME, Specialised Lending, Bank, Sovereign, Mortgage, Auto Loan, Unsecured and Retail SME, including Probability of Default (PD), Loss Given Default (LGD) and Exposure at Default (EAD) models
- Application, Behavioral and Collection Scorecards for Retail Exposures
- Credit Concentration Risk Model
- Review and development of Counterparty Credit Risk (CCR) policies, processes, methodology and reporting requirements.
- Define framework and procedures for the conduct of credit stress testing, including policy, methodology, design of test scenarios and risk parameters, development of reports on outcome of test, etc.
- Assist banks in performing credit review of selected samples of credit cases, and provide our inputs and recommendations for follow-up actions.
- Provide advice on Credit Portfolio Management approaches, strategies, system functionalities and reporting requirements.
- Development of aging and classification policies, as well as effective collection strategies based on the bank’s loss and recovery experience, and enhancement of collections and NPL management capabilities.
Overview
Market risk is the risk of losses arising from on and off-balance-sheet positions due to movements in market prices. Based on Basel principles, such risks include the risks pertaining to interest rate-related instruments and equities in the trading book, and foreign exchange risk and commodity risk throughout the bank (ie, in both trading and banking books).
As stipulated by Basel, banks are allowed to adopt either of the two approaches for computing regulatory market risk capital: the Standardized Approach (SA) and the Internal Model Approach (IMA).
Our Services
Our Services in relation to Market Risk Management include the following:
- Assessment of the bank’s current systems and practices against requirements under the Fundamental Review of Trading Book (FRTB)
- Review and/or development of market risk policies and guidelines.
- Development of framework and procedures for effective Market Risk Management.
- Development of user specifications and systems functionalities for market risk systems.
- Model validation (including back-testing) of:
- Pricing and Valuation Models
- VaR Models
- Market risk systems such as Murex, Numerix, RiskManager, Kamakura, Algorithmics, Kondor+, KGR, Summit and WallStreet.
- Front-office to Back-office review of Treasury Controls, including:
- Governance and Policies
- Setting and Calibration of Risk Limits to Risk Appetite
- Product Control and Valuation
- P&L Attribution and Reconciliation
- Position Reconciliation
- Valuation Adjustments / Reserves
- Risk Monitoring and Reporting
- Settlements
- Collateral Management
- Review of IMA Compliance
- Stress Testing
Overview
Operational risk refers to the risk of loss resulting from inadequate or failed internal processes, people and systems or from external events. The main types of operational risk include:
- Internal and external fraud
- Employment practices and workplace safety
- Clients, products and business practices
- Damage to physical assets
- Business disruption and system failures (including hardware/software/network failures, security breaches in network and systems and other cybersecurity incidents, etc)
- Execution, delivery and process management
Our Services
We provide the following consulting services to banks in the area of ORM:
- Assess the bank’s current operating environment to map out the scope of changes required for the bank in various aspects of ORM, including the various Basel approaches for operational risk.
- Develop a Framework for Monitoring and Reporting of Operational Risks, covering areas such as Key Operational Risk Indicators, Risk and Control Self-Assessment Processes, Operational Loss Reporting Processes and setting up of Loss Events Database.
- Review and enhance/develop a Technology Risk Management Framework, covering Application Risk, Infrastructure Risk, Process Risk, IT Management Risk and overall IT governance and control framework.
- Review and develop ORM Policies, such as New Product Program Policy, Business Continuity Policy and Plans, Technology Risk Management Policy, Outsourcing Policy and Anti-money Laundering Policy, etc.
Overview
Liquidity, or the ability to fund increases in assets and meet obligations as they fall due, is crucial to the ongoing viability of any banking organization.
The gap between the maturity structure of a bank’s assets (such as loans and investments) and liabilities (such as deposits) requires careful management in order to ensure that the bank meets all funding obligations.
Sound liquidity management helps to reduce the probability of the bank facing serious liquidity problems and thus causing a liquidity crisis which would eventually affect the viability of the bank.
Our Services
We provide the following services to help our clients meet the required objectives:
- Review the bank’s current Liquidity Risk Management policies and practices, and provide our recommendations on how the bank can further enhance this function.
- Develop a proper risk governance and organization structure to support Liquidity Risk Management.
- Develop policies, processes and guidelines for managing liquidity risk.
- Provide recommendations to banks on liquidity risk measurement requirements such as Liquidity Coverage Ratio (LCR) and Net Stable Funding Ratio (NSFR).
- Provide a comprehensive set of liquidity risk reports for banks to monitor and assess its liquidity risk exposure.
- Develop a set of policy and processes for conducting liquidity stress testing.
- Develop models for projecting the bank’s potential cash flows arising from each balance sheet item.
- Develop appropriate funding contingency plan that details the range of actions to be taken by the bank under the various stress scenarios.
Overview
Under the Basel capital framework, interest rate risk in the banking book has been identified as one of the important issues that banks should have a comprehensive governance and risk management framework to manage.
Banking book interest rate risk refers to the exposure of a bank’s financial condition to adverse movements in interest rates, and is commonly assessed from 2 different perspectives: the earnings perspective and the economic value perspective.
A robust interest rate risk management framework should be instituted to ensure that the banking book interest rate risk is actively managed.
Our Services
Our consulting services in relation to Banking Book Interest Rate Risk Management include:
- Review the bank’s current interest rate risk management policies and practices, and provide our recommendations on how the bank can further enhance this function.
- Define the roles and responsibilities of various organisational units responsible for Banking Book Interest Rate Risk Management.
- Review existing policies and guidelines, established by the bank for managing its interest rate risk so as to ensure that all key aspects of the risk management processes are addressed in the policies and guidelines.
- Review impact of the implementation of IFRS 9 accounting standard on the banks’ interest rate risk management and reporting.
- Develop methodology for measuring impact on net interest income (NII) and economic value of equity (EVE), including selection of the appropriate interest rate curves, construction of the interest rate scenarios, construction of balance sheet growth scenarios, etc
- Formulate procedures for conducting stress tests on the bank’s interest rate risk, including the construction of the appropriate stress scenarios.
Overview
The pandemic has been a catalyst for digital transformation, incentivising organisations to pivot to digital channels, adopt large-scale remote working, and transform products and services through extensive digitalisation initiatives to better meet the changing needs of customers.
Amid myriad advantages of digitalisation, including improved operational efficiency and customer experience, there are risks that an organisation may be exposed to in a digital environment. Digital risk refers to unexpected consequences arising from digital transformation initiatives. Such risks – cybersecurity risk, fraud risk, data privacy risk, third-party risk and other forms of digital risk – can disrupt an organisation’s progress towards achieving desired business objectives.
In the face of these challenges, managing potential digital threats have become increasingly crucial as failure to address them can lead to regulatory scrutiny, reputational damage, erosion of customer confidence, financial losses and high-profile legal exposure. To manage such risks effectively, organisations need to build a culture of digital resilience, strengthen their capabilities and controls over the use of digital technology, and significantly improve cybersecurity measures and processes..
Our Services
Our services in relation to Digital Risk Management include the following:
- Formalise a robust digital risk governance framework to streamline digital development and centralise approval procedure by clearly defining accountability and decision-making authority for digital strategy, policy and standards.
- Conduct risk assessments to understand banks’ digital footprint, assess their digital risk profile and create a register of potential digital risk hotspots, with a focus on addressing top digital risk priorities.
- Review banks’ current control environment for digital initiatives to identify gaps and enhance the efficiency of their IT controls and processes in preserving confidentiality, integrity and protection of data and systems.
- Establish appropriate processes for due diligence and risk management of third-party digital risks, including vendor/partner selection standards for new technology or system acquisition and ongoing monitoring of outsourced operations.
- Design business continuity and disaster recovery plans in preparation for and response to digital crises or system-related issues that banks are susceptible to, or improve banks’ current business continuity capabilities to be cyber resilient.
- Provide cybersecurity and data privacy awareness training to help banks mitigate digital risks and continue to digitalise safely and securely in compliance with regulatory requirements and best practice digitalisation standards.
